As cloud computing becomes the backbone of modern applications, security and isolation are more important than ever. That’s where VPCs (Virtual Private Clouds) come in.
In this post, we’ll demystify what a VPC is, why it matters, and how you can use it to build secure, scalable infrastructure in the cloud.
What is a VPC?
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a logically isolated section of a cloud provider’s network (like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure) where you can launch your cloud resources (like servers, databases, and containers) in a virtual network that you control.
Think of it like building your own private data center — but in the cloud.
Architecture of VPC:
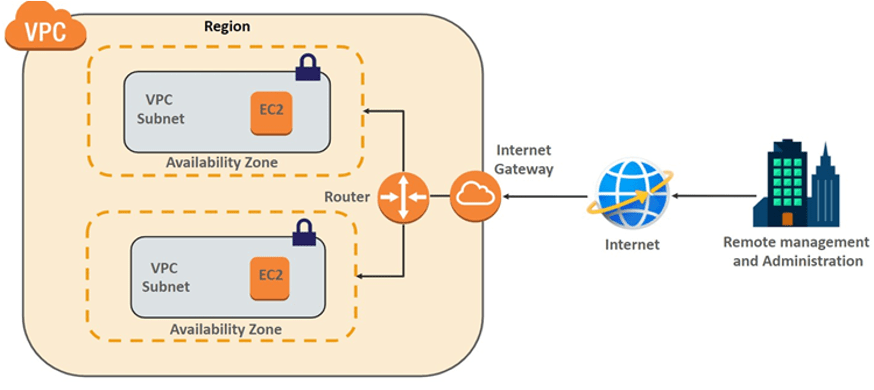
Key Features of a VPC
- Isolation: Your VPC is completely isolated from other users on the cloud platform.
- Custom IP Address Ranges: You can define your own IP ranges using CIDR blocks (e.g., 10.0.0.0/16).
- Subnets: Break your VPC into smaller network segments (public and private).
- Route Tables: Control traffic flow within your VPC and to the internet.
- Internet Gateways (IGW): Provide internet access to public subnets.
- NAT Gateways: Allow instances in private subnets to access the internet without being exposed.
Real-World Example
Let’s say you’re building a web application with a frontend, backend, and database. In your VPC setup, you might do something like this:
- Public Subnet: Contains a load balancer and web servers (accessible from the internet).
- Private Subnet: Hosts backend services and databases (not directly accessible from the internet).
- NAT Gateway: Lets your backend services fetch updates or send outbound traffic securely.
Benefits of Using a VPC
- Enhanced Security: Control inbound/outbound traffic using security groups and NACLs.
- Scalability: Add or modify subnets and services without re-architecting everything.
- Flexibility: Connect to on-prem data centers using VPN or Direct Connect.
- Compliance: Meet strict data privacy and regulatory requirements.